research
1. Real-Time MRI / Fast MRI (Cardiovascular)
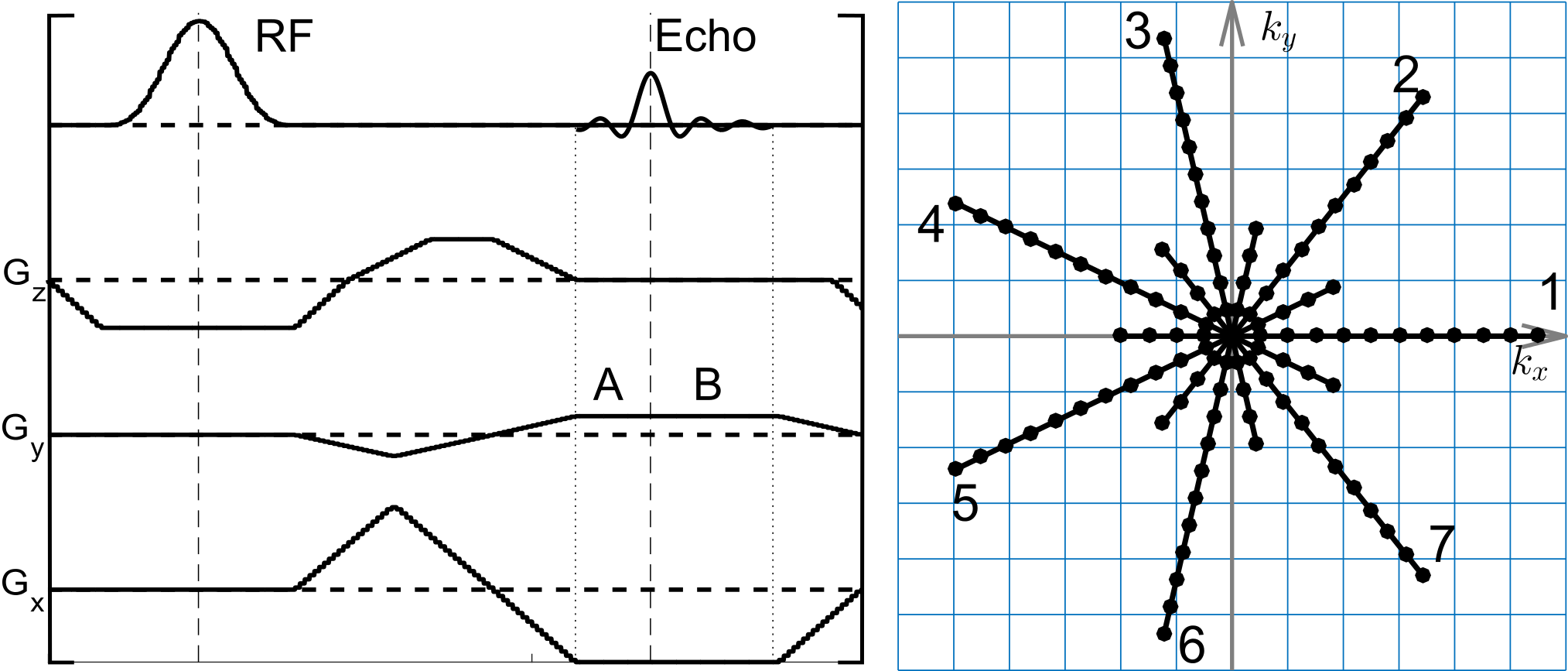
Asymmetric-Echo Radial Sampling (i.e. Partial Fourier)
-
Asymmetric-echo readout shortens echo time and is beneficial when combined with flow-compensation and -encoding gradients.
-
Overlapping of flow gradients with pre-dephasing and/or slice-rewinder gradients further reduces TE.
Aortic Blood Flow Quantification
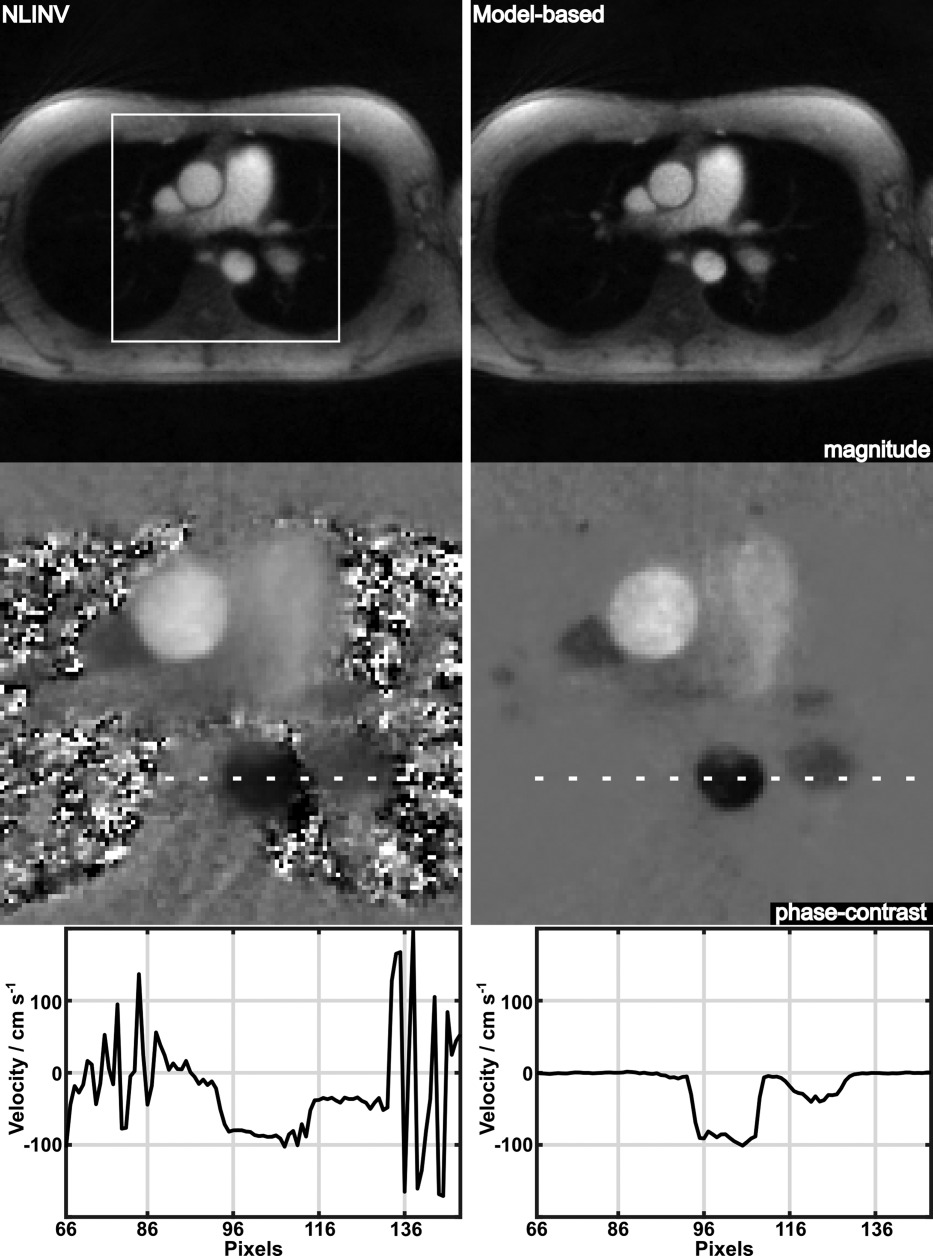
-
The model-based reconstruction directly and jointly estimates the magnitude and the phase-difference image from acquired k-space data.
-
With proper regularization on the phase-difference map, the model-based reconstruction largely removes random phase noise in the background, which appears from the conventional phase difference calculation between two images.
2. Multi-Echo Radial Sampling
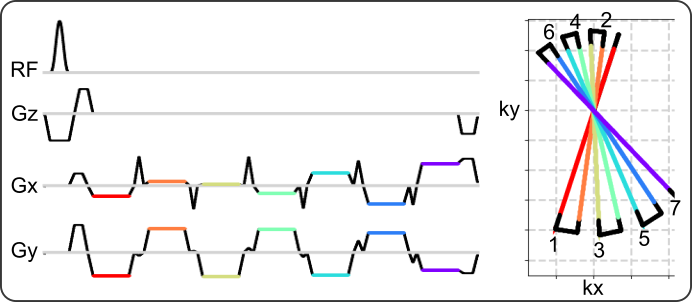
-
In analogy with the famous echo-planar imaging (EPI), multi-echo radial samples multiple echoes at different k-space radial spokes per radio frequency (RF) excitation.
-
It can be applied to water/fat separation, functional MRI, quantitative T2* mapping, and even diffusion/susceptibility imaging (under development).
-
Multi-echo radial sampling has been integrated with stack-of-stars as well as symmetric echo acquisition for volumetric and multi-dimensional imaging. See below for an example of the stack-of-stars acquisition on the NIST phantom and NUFFT reconstruction:

Application #1: Liver Fat, R2* and B0 Field Mapping
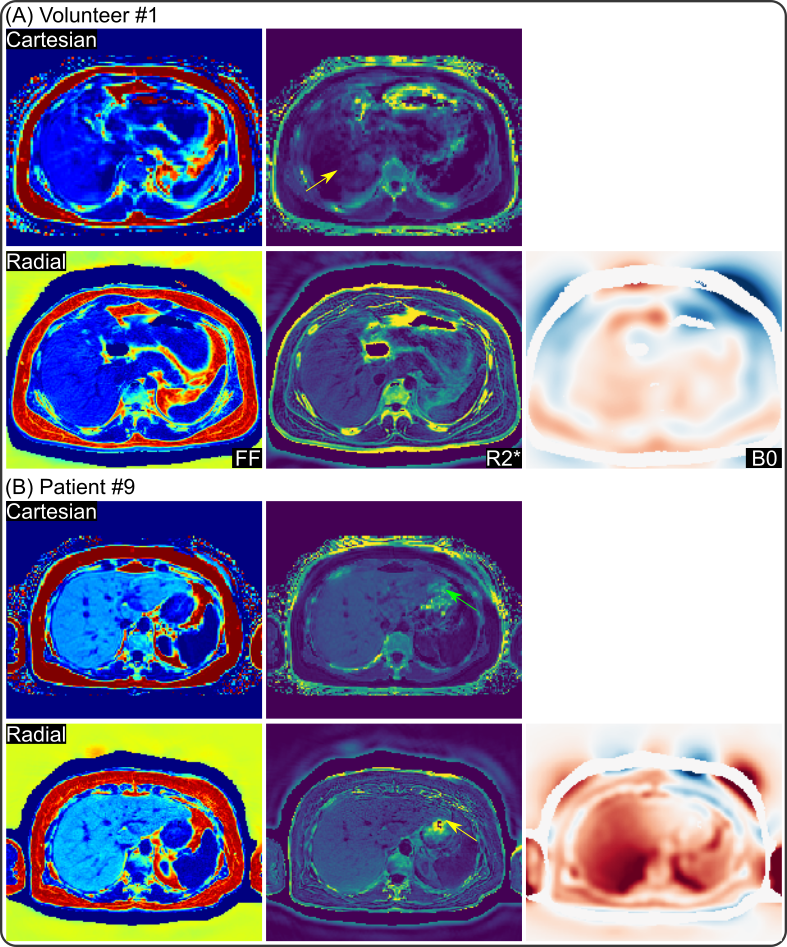
-
Joint estimation based on iteratively regularized Gauß-Newton method (IRGNM) and alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) to allow for generalized regularization.
-
Free-breathing liver fat and R2* mapping in 2 minutes for 3D acquisition.
-
Respiratory motion is resolved with the SSA-FARY self-gating technique.
Application #2: T2*-weighted imaging (Brain)

3. Diffusion MRI
NAViEPI
NAViEPI with consistent ESP between imaging and navigator echoes: where interleaved EPI meets readout-segmented EPI
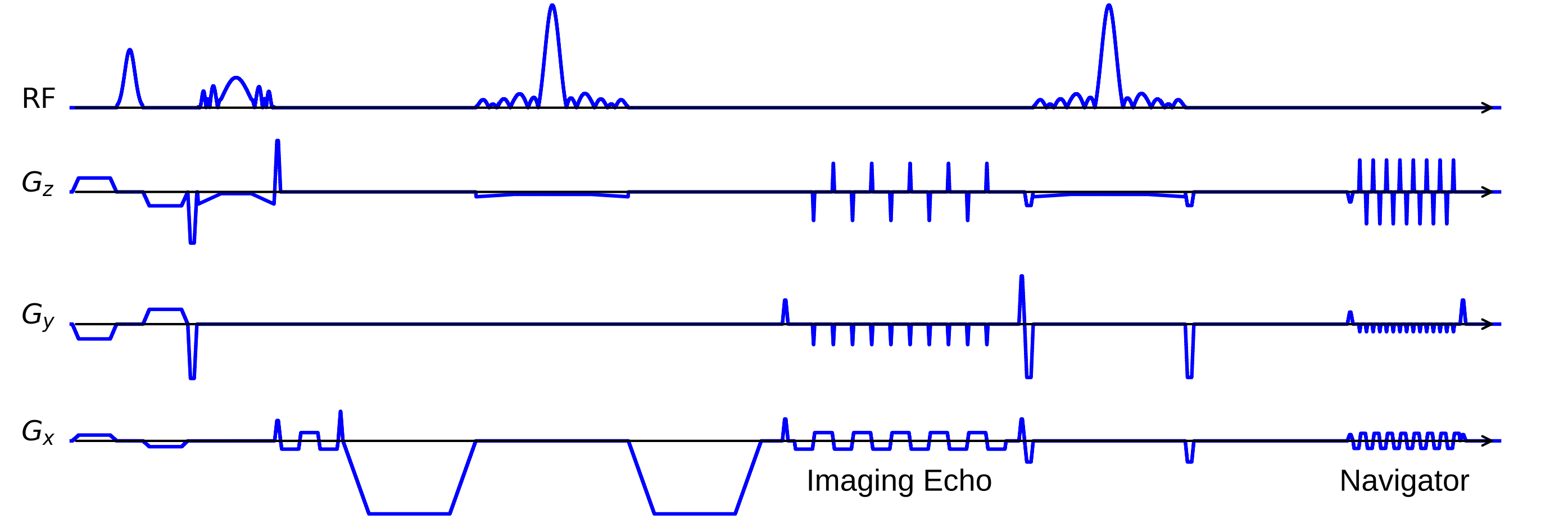
-
NAViEPI features:
- accelerated multi-shot EPI;
- shifted encoding among diffusion-encoding directions.
-
NAViEPI enables:
- minimal distortion mismatch between echoes;
- flexible number of shots for sub-millimeter mesoscale resolution;
- reliable shot-to-shot phase estimation from navigators.
Generalized joint k-q-slice reconstruction
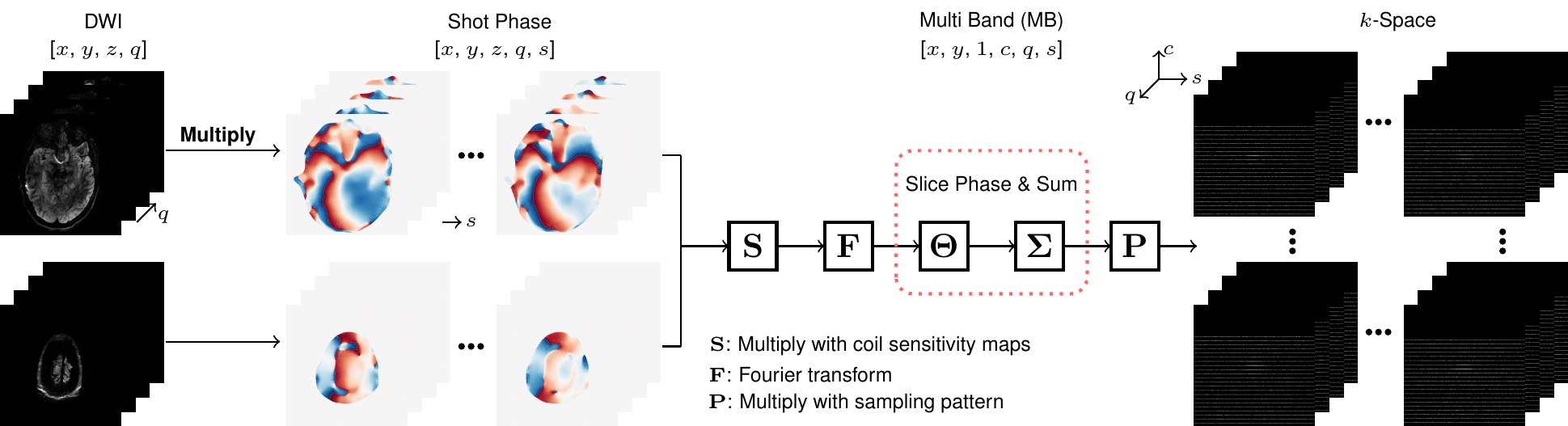
Example: 7T Brain Diffusion MRI
- Data: hosted on Zenodo
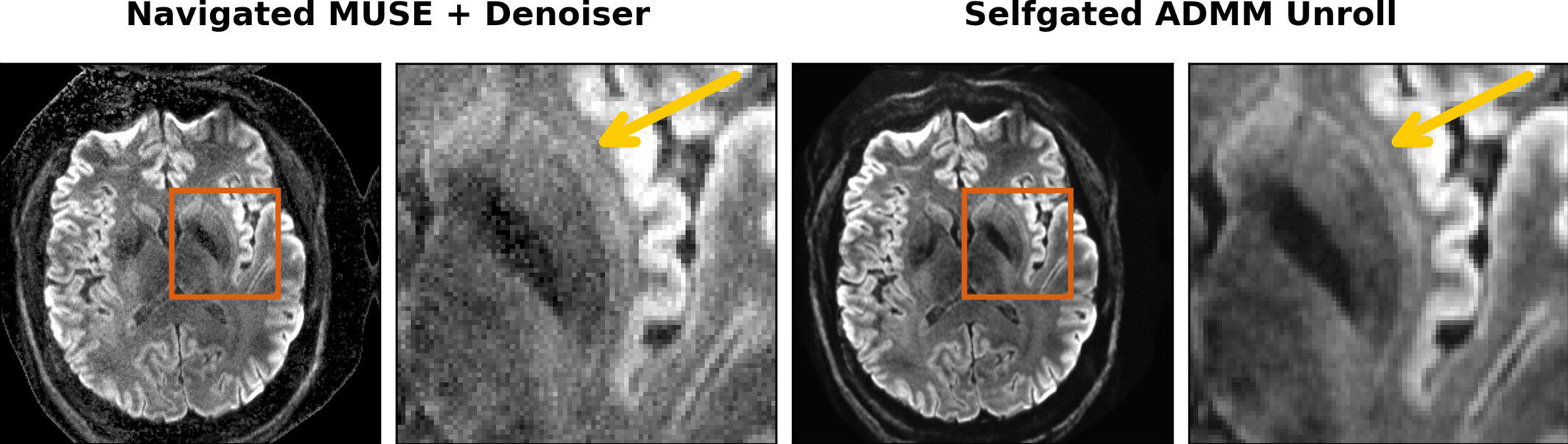
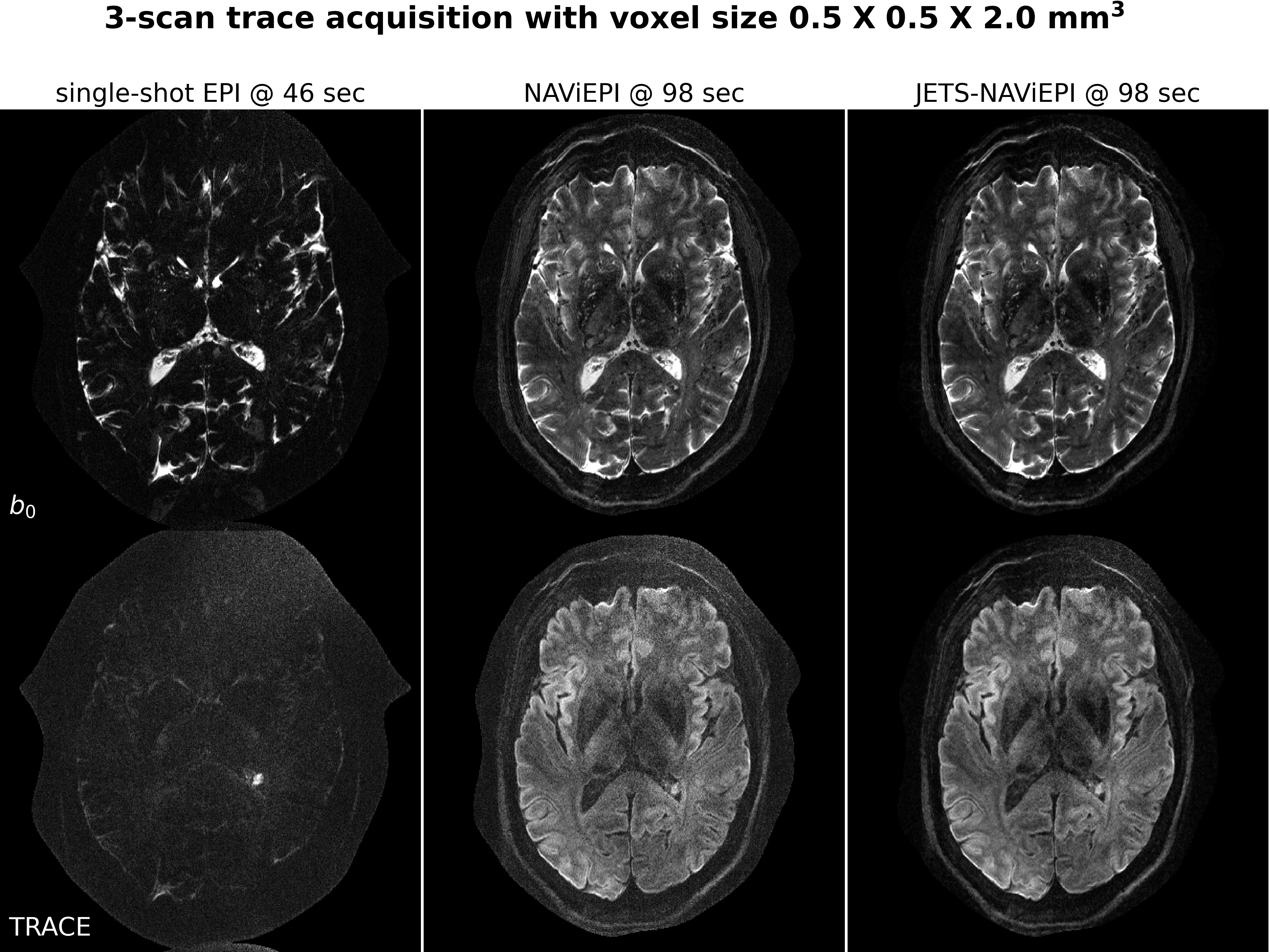
Self-Supervised ADMM Unrolling Reconstruction
ADMM Unrolling enables submillimeter DWI based on multi-band multi-shot interleaved EPI acquisition.
Example: 0.7 mm isotropic resolution DWI with the proposed self-gated ADMM unrolling enables the visualization of the tiny structure claustrum